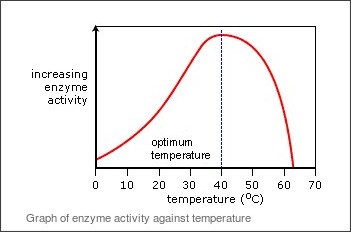
Enzymes are matters made of protein that help stimulate chemical reactions. Like most chemical reactions, the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction increases as the temperature is raised.
The enzyme activity gradually increases with temperature up to around 37ºC, or body temperature. But as the temperature continues to rise, the rate of reaction falls rapidly as heat energy denatures the enzyme.
Enzymes work slowly at low temperatures too – but this is because the substrate molecules have less energy and move into the active site more slowly. This is not a permanent change.
Learn more about enzymes by checking these 10 cool facts shared by Renewlife.com.